The most important things to know about nutrition when trying to conceive:
- Unsaturated fatty acids support hormone production and reduce inflammation in the body.
- Complex carbohydrates stabilize blood sugar and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
- Antioxidants protect eggs and sperm.
- Omega-3 fatty acids improve egg implantation and promote sperm quality in men.
- Sugar, caffeine, alcohol and trans fats have a negative effect on fertility.
The right diet when trying to conceive and during pregnancy
A healthy diet plays a crucial role when it comes to supporting fertility and increasing the chances of successful conception. So what should women trying to conceive actually eat in order to get pregnant? And what should men pay attention to in their diet?
The following nutritional tips can support you if you are trying to conceive and contribute to a healthy pregnancy.
A balanced diet for optimal fertility
A healthy lifestyle with a varied and balanced diet plays an important role, especially for couples who are trying to conceive. The following factors support a balanced diet:
Healthy fats
Foods rich in healthy fats such as avocados, nuts and olive oil contain essential fatty acids that are important for hormonal balance. Unsaturated fatty acids in particular, which are found in oily fish such as salmon and mackerel, but also in high-quality rapeseed oil, can support fertility and reduce inflammation in the body.
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates from whole grain products, vegetables and pulses ensure stable blood sugar regulation. Oatmeal, for example, is a great start to the day. This is particularly important as high blood sugar levels and insulin resistance can impair fertility.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants such as vitamin C, selenium and zinc protect the cells from oxidative stress. A diet rich in fresh fruit and vegetables helps to fight free radicals and improve overall cell health. Berries and broccoli can make an important contribution here.
The importance of nutrient supply
An optimal supply of high-quality micronutrients and trace elements is crucial for improving egg quality.
As the supply of nutrients from food is often not sufficient to significantly improve egg quality, it is recommended and scientifically proven to take additional high-quality dietary supplements.
This compensates for potential deficiencies, stimulates ovarian activity and supports follicle maturation. Clinical studies have shown improved blastocyst rates and higher pregnancy rates after taking the following active ingredients for at least three months:
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have a positive effect on fertility in both men and women.
In women, omega-3 fatty acids can regulate hormone production and improve inflammation in the endometrium, which increases the chances of successful fertilization and implantation. Women who took omega-3 supplements were 1.51 times more likely to become pregnant compared to those who did not. 1
In men, omega-3 fatty acids help improve sperm quality by optimizing sperm motility and shape and reducing oxidative damage. In addition, they promote healthy blood flow, which is important for normal erectile function.
Folic acid
Folic acid is an essential B vitamin that plays a crucial role in cell division and growth. It is particularly important for the development of the neural tube in the unborn child, which is why a sufficient supply before pregnancy is of great importance in order to prevent neural tube defects.
In women who are trying to conceive, folic acid supports the healthy development of eggs and can promote the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Folate can also be obtained naturally from food. Good sources of folate include green leafy vegetables, pulses and whole grain products.
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) promotes fertility through its strong antioxidant effect and its ability to eliminate toxins from the body.
In women, NAC can improve fertility by reducing oxidative stress damage, which is important for egg health and hormonal balance. In addition, NAC can improve insulin sensitivity and thus regulate hormone balance, which can lead to ovulation induction, especially in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In scientific studies, NAC has shown improved pregnancy rates in IUI cycles. 2
In men, NAC helps improve sperm quality by reducing oxidative damage to sperm, increasing sperm motility and increasing total sperm count. Through these positive effects on cell health and hormone regulation, NAC may increase the chances of successful conception in both men and women.
Alpha lipoic acid
A scientific study shows the positive effects of alpha lipoic acid on both female and male fertility.
Improvements range from egg maturation to fertilization, embryo development and potential pregnancy rates. Regular use of alpha-lipoic acid in both subfertile women and men has been shown to reduce pelvic symptoms of endometriosis, regulate the menstrual cycle and metabolic disorders, and improve sperm quality. 3
Trans-resveratrol
Trans-resveratrol has a therapeutic effect in men with idiopathic infertility. A pilot study suggests that trans-resveratrol has a positive effect on sperm concentration, total sperm count and total and progressive motility without affecting sperm morphology, ejaculate volume and pH.4
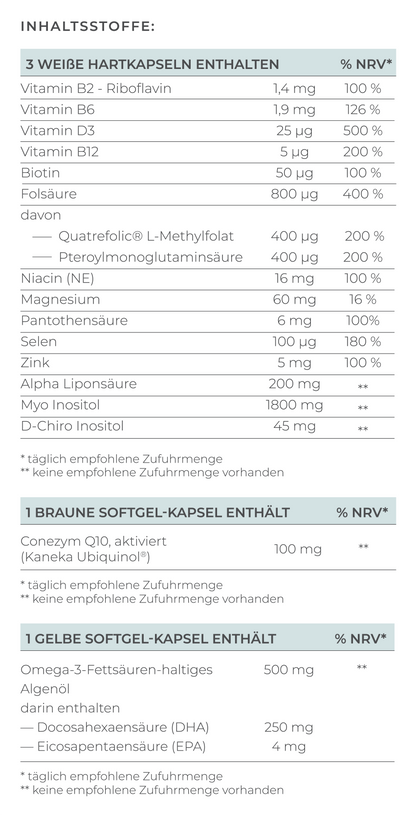
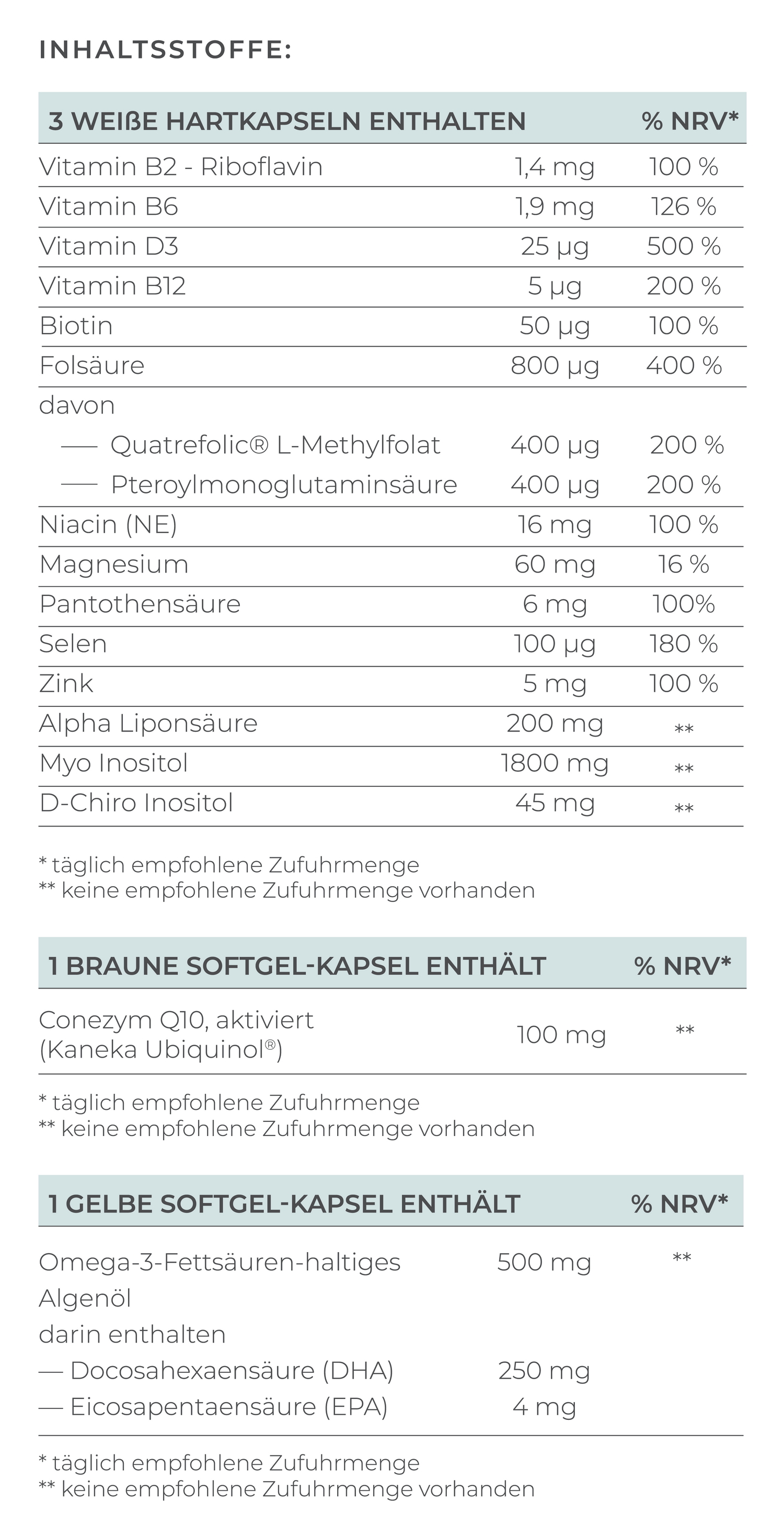
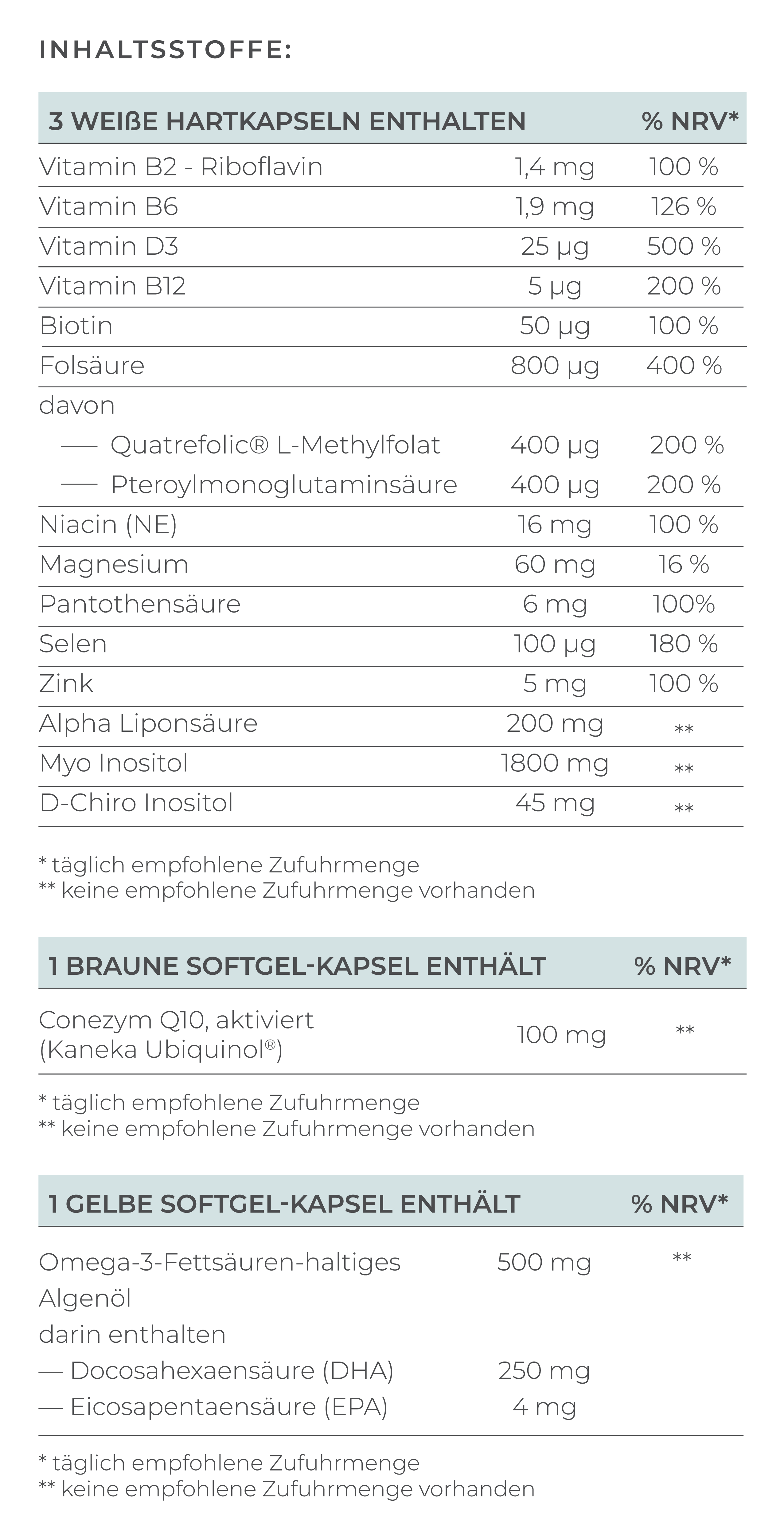
The active ingredients mentioned are only part of the important nutrients required for optimal egg and sperm quality. You will find a comprehensive supply of all relevant nutrients in VILAVIT Female and VILAVIT Male.
Foods to avoid
Some foods can have a negative impact on fertility and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether:
Sugary foods
Sugary drinks and foods can have a negative impact on fertility as they can lead to a variety of health problems that affect reproductive health. High sugar consumption can lead to insulin resistance and increased blood sugar levels, which in turn can cause hormonal imbalances. In women, this can lead to disruption of the female cycle and reduced egg quality, while men may experience reduced sperm quality.
In addition, sugary foods often promote obesity, which is an additional risk factor for infertility. In the long term, excessive consumption of sugar can contribute to chronic inflammation, which can affect the reproductive organs.
It is therefore advisable to reduce the consumption of sugar and focus on a balanced, nutrient-rich diet to support fertility.
Caffeine
Scientific studies on caffeine consumption when trying to conceive are inconclusive. However, there is some evidence that high coffee consumption may prolong the time to pregnancy and affect fetal development, although the mechanism for this is unclear. Caffeinated drinks such as coffee or energy drinks could affect ovulation and the function of the corpus luteum by altering hormone levels.5
Despite the available data, we recommend limiting caffeine intake to a maximum of 200 milligrams per day.
Alcohol
Alcohol is a potent neurotoxin that can have a significant impact on our health not only during pregnancy, but also when we are trying to conceive. Alcohol consumption when trying to conceive can have a negative impact on fertility in both women and men and reduce the chances of pregnancy.
A meta-study of over 27,000 women showed that women who consumed more than seven drinks per week (around 84g of alcohol) were 7% less likely to become pregnant after IVF treatment. Male alcohol consumption also has a negative effect on the live birth rate.
Trans fats
Trans fats, which are found in many processed foods and fast food, can disrupt hormone production. In women, the intake of TFAs (trans fatty acids) is associated with an increased risk of non-ovulation, has a negative effect on the duration of pregnancy and can lead to fetal development defects and miscarriages. Women with endometriosis in particular should ensure that their diet is as low in trans fats as possible, as trans fats are associated with increased levels of inflammation in the body, which can exacerbate the symptoms of the disease.
In men, clinical studies also suggest that trans fat intake is inversely related to sperm concentration and total sperm count and has a positive correlation with asthenospermia. 7
Additional tips to promote fertility
Stay hydrated
Adequate hydration is important for overall health and fertility. Without enough water, men can suffer from low semen volume and women from persistent vaginal dryness. 8
Drink enough water every day to keep the body well hydrated.
Maintain a healthy body weight
A healthy body weight is crucial for fertility. Studies have shown that both a BMI that is too low and one that is too high pose a potential risk of infertility in women. The cause is often hormonal imbalances. 9
Women who are overweight or obese take longer to become pregnant and have a reduced fertility rate, an increased need for gonadotropins and a higher miscarriage rate compared to women of normal weight. Male obesity can lead to subfertility, increased testicular temperature, impairment of the physical and molecular structure of sperm, reduced sperm quality and erectile dysfunction due to peripheral vascular disease. 5
Therefore, a balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial when trying to conceive.
Stress management
Higher stress levels, measured by salivary alpha-amylase levels, are associated with a longer time to conception and an increased risk of infertility. 6
In addition to a healthy diet, you should also focus on stress management strategies such as yoga, meditation or regular walks.
Conclusion: A healthy diet supports fertility
The right diet is an important building block on the path to conceiving. A balanced and nutritious diet not only supports general health, but also fertility. By paying attention to high-quality micronutrients for egg quality and sperm quality, avoiding processed foods and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, you create the best conditions for successful conception.
Frequently asked questions
Which foods promote the desire to have children?
A balanced diet can have a positive effect on fertility and support both egg quality and sperm health. Healthy fats in particular, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil and fatty fish such as salmon, play an important role in hormone production. Antioxidant foods such as berries, dark chocolate, green leafy vegetables and nuts can also help to reduce oxidative damage to eggs and sperm.
An adequate supply of vitamin D, which is found in eggs, fish and fortified dairy products, is essential for a stable hormone balance. In addition, complex carbohydrates from whole grain products, pulses and vegetables support blood sugar regulation and have a positive effect on the menstrual cycle. Iron-rich foods such as spinach, lentils and red meat can help to replenish iron stores and thus promote the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Sperm quality also benefits from a nutrient-rich diet. Foods with a high zinc content, such as oysters, pumpkin seeds and whole grain products, promote sperm production, while selenium-rich foods such as Brazil nuts and fish can improve sperm motility. In general, a healthy and varied diet low in sugar and processed foods is one of the best ways to support fertility naturally.
Sources:
- Stanhiser J, Jukic AMZ, McConnaughey DR, Steiner AZ. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and fecundability. Hum Reprod. 2022
- Bedaiwy et al., N-acetyl cystein improves pregnancy rate in long standing unexplained infertility: A novel mechanism of ovulation induction, 2004
- Di Tucci C, Galati G, Mattei G, Bonanni V, Capri O, D'Amelio R, Muzii L, Benedetti Panici P. The role of alpha lipoic acid in female and male infertility: a systematic review. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2021
- Illiano E, Trama F, Zucchi A, Iannitti RG, Fioretti B, Costantini E. Resveratrol-Based Multivitamin Supplement Increases Sperm Concentration and Motility in Idiopathic Male Infertility: A Pilot Clinical Study. J Clin Med. 2020
- Lucero J, Harlow BL, Barbieri RL, Sluss P, Cramer DW. Early follicular phase hormone levels in relation to patterns of alcohol, tobacco, and coffee use. Fertil Steril. 2001
- Do caffeine and alcohol affect fertility treatments? Saudi Med J. 2022 Nov;43
- Çekici H, Akdevelioğlu Y. The association between trans fatty acids, infertility and fetal life: a review. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2019
- Zhu L, Zhou B, Zhu X, Cheng F, Pan Y, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Xu Q. Association Between Body Mass Index and Female Infertility in the United States: Data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013-2018
- Emokpae MA, Brown SI. Effects of lifestyle factors on fertility: practical recommendations for modification. Reprod Fertil. 2021
- Lynch CD, Sundaram R, Maisog JM, Sweeney AM, Buck Louis GM. Preconception stress increases the risk of infertility: results from a couple-based prospective cohort study--the LIFE study. Hum Reprod. 2014