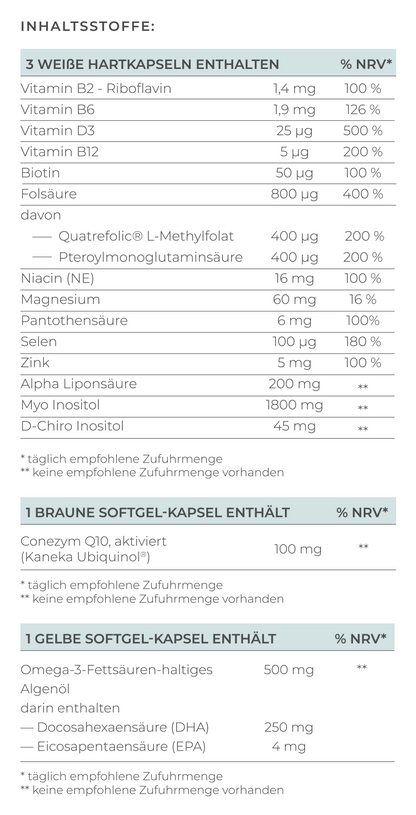
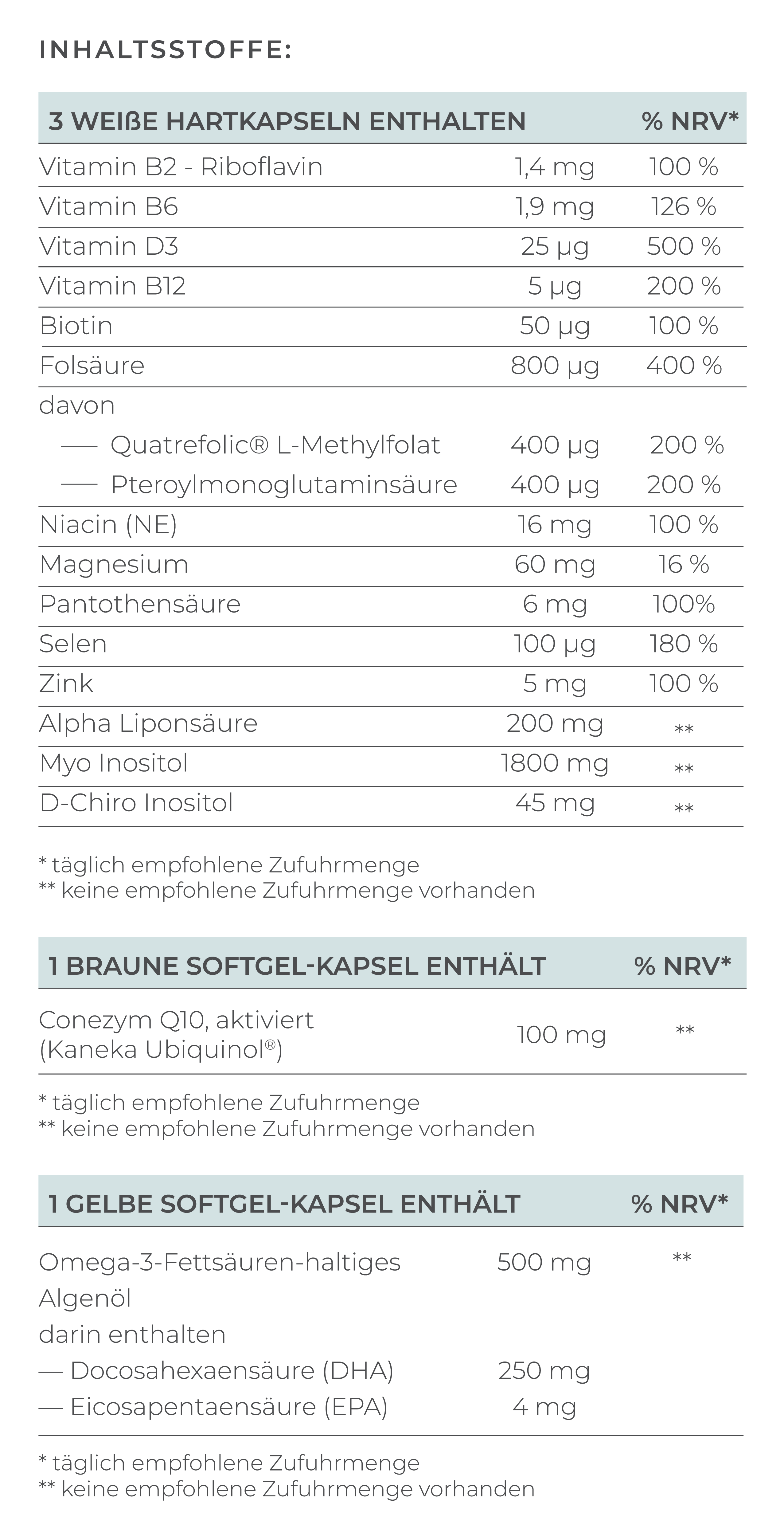
The Essential Nutrients for Fertility at a Glance:
- Folate: The bioavailable form of folic acid is important for the process of cell division.
- Ubiquinol: Promotes egg maturation and protects against oxidative stress. Especially important from the age of 35 for better egg quality.
- Vitamin D: Regulates fertility hormones and improves pregnancy rates with adequate vitamin D levels.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA): Support egg quality, menstrual cycle, and embryo implantation.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid: A powerful antioxidant that protects eggs from oxidative stress and improves IVF success rates.
The nutrient requirements during pregnancy are increased. Important nutrients for fetal growth and development include vitamin A, vitamin D, folate, and omega-3.
A recent study has revealed alarming results: Up to 90% of all women are undernourished when it comes to essential nutrients that can affect not only their overall health but also their fertility (Sauder et al., 2023). This finding highlights the importance of a balanced diet and targeted supplementation for women with fertility concerns.
Nutrients of Particular Importance for Fertility include folate, vitamin D, ubiquinol, omega-3, and antioxidants like alpha-lipoic acid.
Folate: Essential for Cell Division and Pregnancy
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is the bioavailable form of folic acid. It is essential for cell division and embryo growth.
Up to 50% of all women in Europe carry an MTHFR gene mutation, often without knowing it. This genetic change can affect the body’s ability to convert folic acid into the active form 5-MTHF (5-Methyltetrahydrofolate). This is especially important for women trying to conceive or during pregnancy, as folate is essential for cell division and healthy fetal development.
A study explored the relationship between folate intake and female fertility. The results showed that women with higher folate intake were more likely to become pregnant (Cueto et al., 2022).
Similarly, maintaining an adequate folate level before and during pregnancy reduces the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus.
Ubiquinol: Cellular Energy and Egg Quality
Ubiquinol, the active form of coenzyme Q10, plays a critical role in egg maturation as it provides energy for the mitochondria—the "powerhouses" of the cell. It also supports the protection of eggs.
Ubiquinol promotes the following key processes:
-
Energy for cell division and maturation: Eggs undergo numerous cell division processes during development. Since these processes are energy-intensive, healthy mitochondria are essential. Ubiquinol helps ensure that eggs have enough energy for optimal maturation and fertilization.
-
Protection from oxidative stress: Oxidative stress can damage eggs and reduce their quality. Ubiquinol acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting eggs from free radicals caused by environmental toxins, stress, or aging.
-
Improvement of mitochondrial function: As women age, the efficiency of mitochondria in eggs decreases. Studies show that ubiquinol can support this function by improving energy production in mitochondria, which can increase the likelihood of successful fertilization and implantation.
Several studies have shown that coenzyme Q10, especially in its bioactive form ubiquinol, can improve egg quality in women, particularly over the age of 35 (Derbyshire et al., 2024).
Vitamin D: Hormonal Regulation and Fertility
Vitamin D plays an important role in regulating hormones that affect fertility.
A study examined the relationship between vitamin D levels in women of reproductive age and pregnancy rates. The study found that women who took vitamin D for 30-60 days (starting at 1,000 IU per day) had higher pregnancy rates compared to those with vitamin D deficiency (Meng et al., 2023).
Omega-3 Fatty Acids with Antioxidant Effects
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA), play a critical role in female fertility.
For female fertility, DHA is particularly important because it:
-
Improves egg quality and may have a positive effect on egg aging (Nehra et al., 2021).
-
Regulates the menstrual cycle and supports hormone production.
-
Promotes the implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus and leads to better pregnancy rates (Stanhiser et al., 2019).
Alpha-Lipoic Acid with Antioxidant Effects
Alpha-lipoic acid is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells, especially eggs, from free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress.
Studies have shown that alpha-lipoic acid can promote egg maturation, fertilization rates, and embryo development. It also leads to better success rates in IVF treatments (Di Tucci et al., 2021).
Increased Nutrient Requirements During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the demand for certain nutrients increases, particularly vitamin A, vitamin D, folate, and omega-3 fatty acids. Vitamin A is crucial for fetal growth and development. A study showed that vitamin A supplementation during pregnancy can reduce the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. Adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids (250mg DHA per day) supports the neurological development of the fetus.
Conclusion
The importance of a balanced diet and targeted nutrient intake for female fertility cannot be overstated. Nutrients such as folate, vitamin D, ubiquinol, omega-3 fatty acids, and alpha-lipoic acid play a crucial role in improving egg quality, hormonal balance, and overall fertility. Especially for women trying to conceive and during pregnancy, it is essential to ensure adequate intake of these micronutrients to support fertility and minimize the risk of complications. A conscious and targeted diet, along with supplementation with specific nutrients, can therefore make a significant contribution on the path to your desired child.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nutrients for Fertility
What dosage is ideal for supporting fertility?
The optimal dosage of nutrients for fertility can vary depending on individual needs and health conditions. However, the following guidelines are generally recommended:
For women trying to conceive, the following daily doses are recommended:
-
Folate (Vitamin B9): Daily dose of 400-800 µg of folate
-
Vitamin D: Daily dose of at least 1000 IU of vitamin D
-
Ubiquinol: Daily dose of at least 100mg of ubiquinol
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA): Daily dose of 250mg of DHA
Can an overdose of nutrients be harmful?
Excessive intake of certain nutrients can negatively impact fertility. For example, excessive zinc can impair fertility. Therefore, it is important to follow the recommended dosages or take combination supplements like VILAVIT Female with the optimal dosage.
References
Katherine A. Sauder, G Lance Couzens, Regan L. Bailey, Christine W. Hockett, Karen M. Switkowski, Kristen Lyall, Jean M. Kerver, Dana Dabelea, Luis E. Maldonado, Thomas G. O’Connor, Sean CL. Deoni, Deborah H. Glueck, Diane J. Catellier, Selecting a dietary supplement with appropriate dosing for 6 key nutrients in pregnancy, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2023
Stanhiser, Jamie et al., Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and fecundability Fertility and Sterility, 2019Di Tucci C, Galati G, Mattei G, Bonanni V, Capri O, D'Amelio R, Muzii L, Benedetti Panici P. The role of alpha lipoic acid in female and male infertility: a systematic review. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2021