Insemination (Intrauterine Insemination, IUI), also known as artificial insemination, involves introducing specially prepared sperm directly into a woman's uterus through a catheter. The procedure is typically performed during the woman's ovulation to increase the chances of fertilization.
Fertilization of the egg occurs naturally; the difference lies in how the sperm reach the egg. Most women take hormone medications to stimulate egg production and follicle growth. This is a painless and more cost-effective procedure compared to in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Process of Insemination
- Hormonal Stimulation: Typically, a low dose of hormones is administered to stimulate egg production.
- Triggering Ovulation: Follicle growth is regularly monitored via ultrasound. When the follicles reach a certain size (around 18mm in diameter), ovulation is triggered.
- Sperm Preparation: Processing of the sperm sample in the laboratory.
- Insemination: During ovulation, a small semen sample is introduced into the woman's uterus through a thin catheter. This is done without sedation or anesthesia.
- Luteal Phase Support: Progesterone is often administered, either vaginally or orally, to facilitate the embryo's implantation in the uterine lining.
Success Rates of Insemination range between 13% and 30%
Success rates for insemination vary and depend on factors such as the woman's age, sperm quality, and other individual health aspects. Pregnancy rates range between 13% and 30% per cycle.
It's important to note that comparatively less invasive insemination may not be suitable for all fertility issues. Discussing individual circumstances with a fertility expert is crucial.
How to Prepare for Insemination
- Monitor Your Cycle: To increase the chances of successful fertilization, it's important to determine the optimal timing for insemination. Track your cycle using an app and discuss the best timing with your specialist.
- Balanced Nutrition: Diet can positively impact egg quality. Following the Fertility Diet, incorporate nutrient-rich foods like folic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and iron to promote reproductive health. Focus on consuming healthy proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Active Lifestyle: Regular exercise can stimulate blood circulation, reduce stress, and regulate hormone levels.
- Adequate Sleep: A healthy sleep routine is crucial for hormonal balance in women and sperm maturation in men.
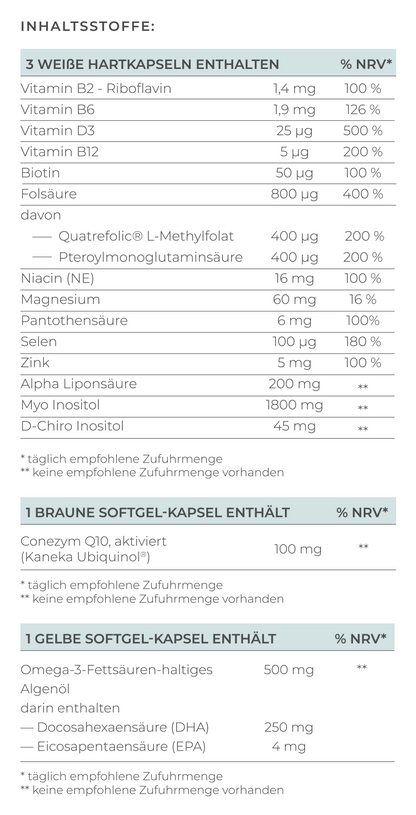
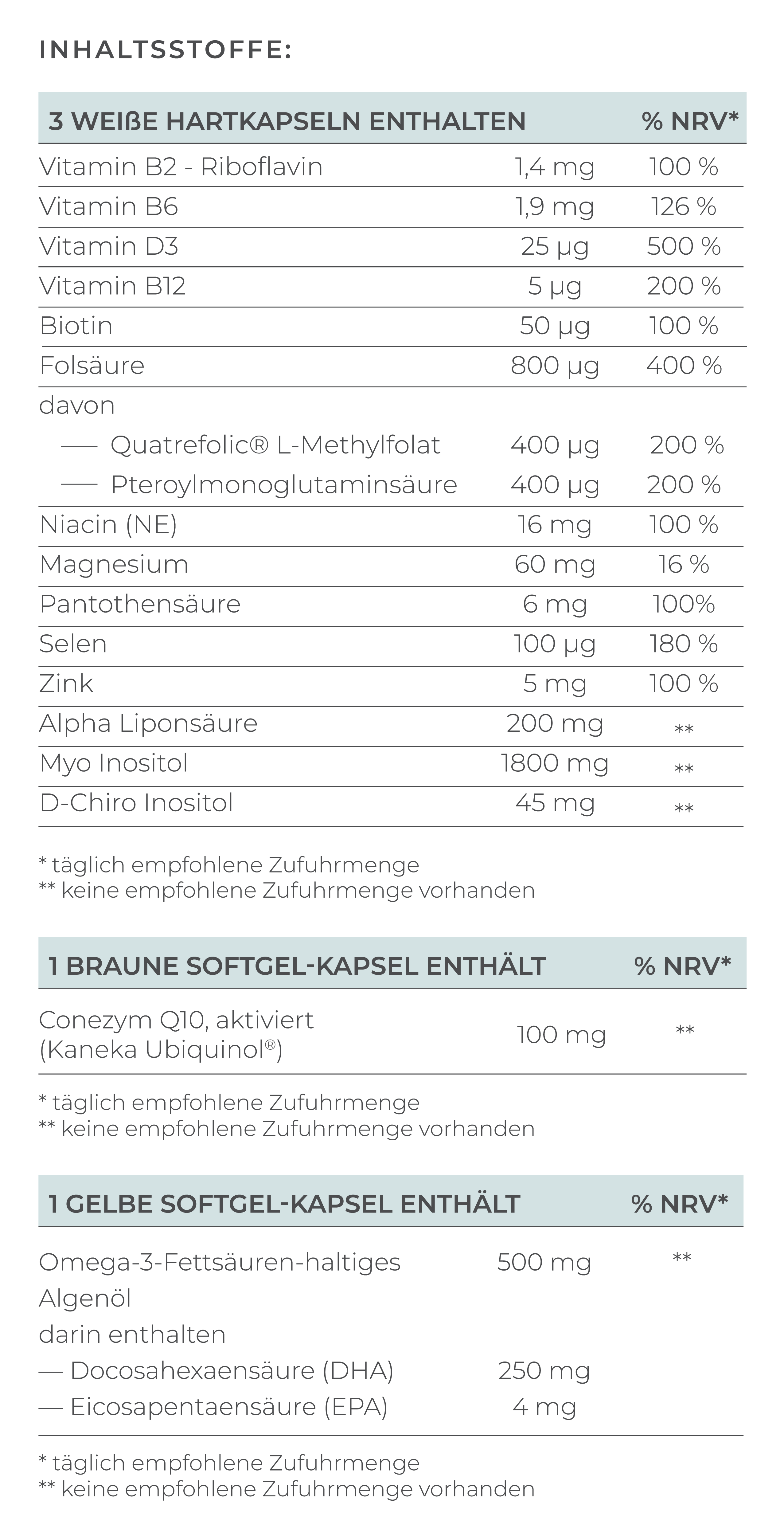
- Pimp my Eggs and Pimp my Sperm: Enhance female and male fertility with micronutrients. Learn how to optimize egg and sperm quality in advance.
- Stress Reduction: Try to avoid stress and practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga.