- According to the WHO, one in six couples experiences an unfulfilled desire for children.
- The causes lie equally with the man and the woman.
- A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and sufficient exercise can positively influence fertility.
- Certain vitamins and micronutrients can support the fertility of both men and women.
- Psychological counseling centers, self-help groups, or online communities can support couples during their fertility journey.
A Major Emotional Challenge
The desire to become parents is one of the deepest and most important life dreams for many couples and a central part of their family planning. However, sometimes things don't go as planned, and the hoped-for pregnancy doesn't happen right away.
An unfulfilled desire for children is an enormous emotional challenge and psychological burden. What makes it even harder is that this topic is still taboo in our society. There's a lack of honesty, experience, and empathy. That's why we want to talk openly about it here and explain what possible next steps are if you are still involuntarily childless.
Causes for Not Getting Pregnant
The reason why involuntary childlessness is rarely talked about is not because it affects no one but because it is still a taboo topic associated with shame and stigma.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), one in six couples is considered infertile. Infertility, also known as infertility, is when a couple does not become pregnant after a year of regular unprotected intercourse (on the woman's fertile days, around ovulation).
The causes are usually diverse and are due to the woman in about 40% of cases, the man in about 40% of cases, and both partners are affected in 20% of cases. (Agarwal, 2015) Often, poor egg quality and/or poor sperm quality is the decisive factor.
The most common causes of an unfulfilled desire for children include:
- Hormonal disorders (e.g., PCOS, hypogonadism)
- Physical causes in women (adhesions due to endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes, fibroids, polyps, changes in the uterus)
- Physical causes in men (antibodies against sperm cells, retrograde ejaculation, azoospermia, impaired testicular function)
- Sexually transmitted diseases (e.g., chlamydia infection)
- Infectious diseases
- Congenital or genetic causes
- Individual lifestyle (exhaustion, stress, diet, lack of exercise, weight problems)
- Age—fertility declines rapidly from the mid-30s
Fertility Is Continually Declining
According to scientific studies, fertility has dropped by over 50% since 1970 and continues to decline annually. (Bongaarts, 2022) Birth rates are also dropping as women decide to become mothers later or less frequently. This is because egg quality declines rapidly with increasing age.
Even in healthy couples with regular unprotected intercourse, the chances of becoming pregnant within the cycle are very low. Depending on age, these chances are usually only 10-30%.
So there is no reason to feel alone with these problems. And there's no reason to bury your head in the sand because fertility can be improved.
What Should I Do If I Can't Get Pregnant?
Here you will learn what to do if you are eagerly waiting for that second line on the pregnancy test.
1. Medical Examination
Couples with an unfulfilled desire for children should definitely undergo a medical examination of both partners to identify possible causes and present treatment options. These include, for example:
- A gynecological examination
-
An ultrasound examination of the woman to check the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and uterine lining
-
A sperm analysis for the man to check sperm quality
-
A blood test of both partners to analyze hormone levels
Similarly, if an infection is suspected, a microbiological examination may be performed, where samples are taken from the vagina or the uterine lining and analyzed in the lab.
The first point of contact is usually the gynecologist for the woman and the andrologist for the man.
A thorough examination and medical history of both partners are crucial for the further treatment plan.
Treatment options range from a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and optimal supply of vitamins and micronutrients to methods of modern reproductive medicine, such as artificial insemination using hormone therapy, insemination, or in vitro fertilization (IVF) or ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection).
2.Adjusting Lifestyle and Diet
An active lifestyle with a healthy diet can positively influence fertility in both men and women. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress, on the other hand, negatively impact pregnancy.
3. Support Through Vitamins & Micronutrients
Scientific studies have shown a positive effect of certain micronutrients on female and male fertility. (Arhin, 2017) The key here is the quality, bioavailability of the active ingredients, and an effective dosage that corresponds to scientific studies.
Important nutrients for women are:
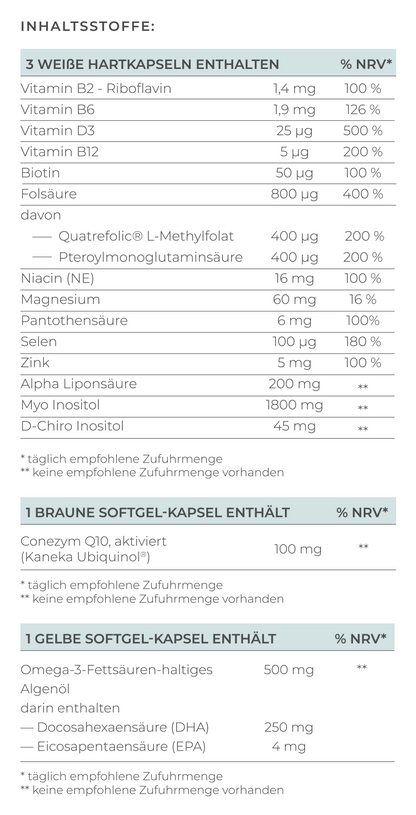
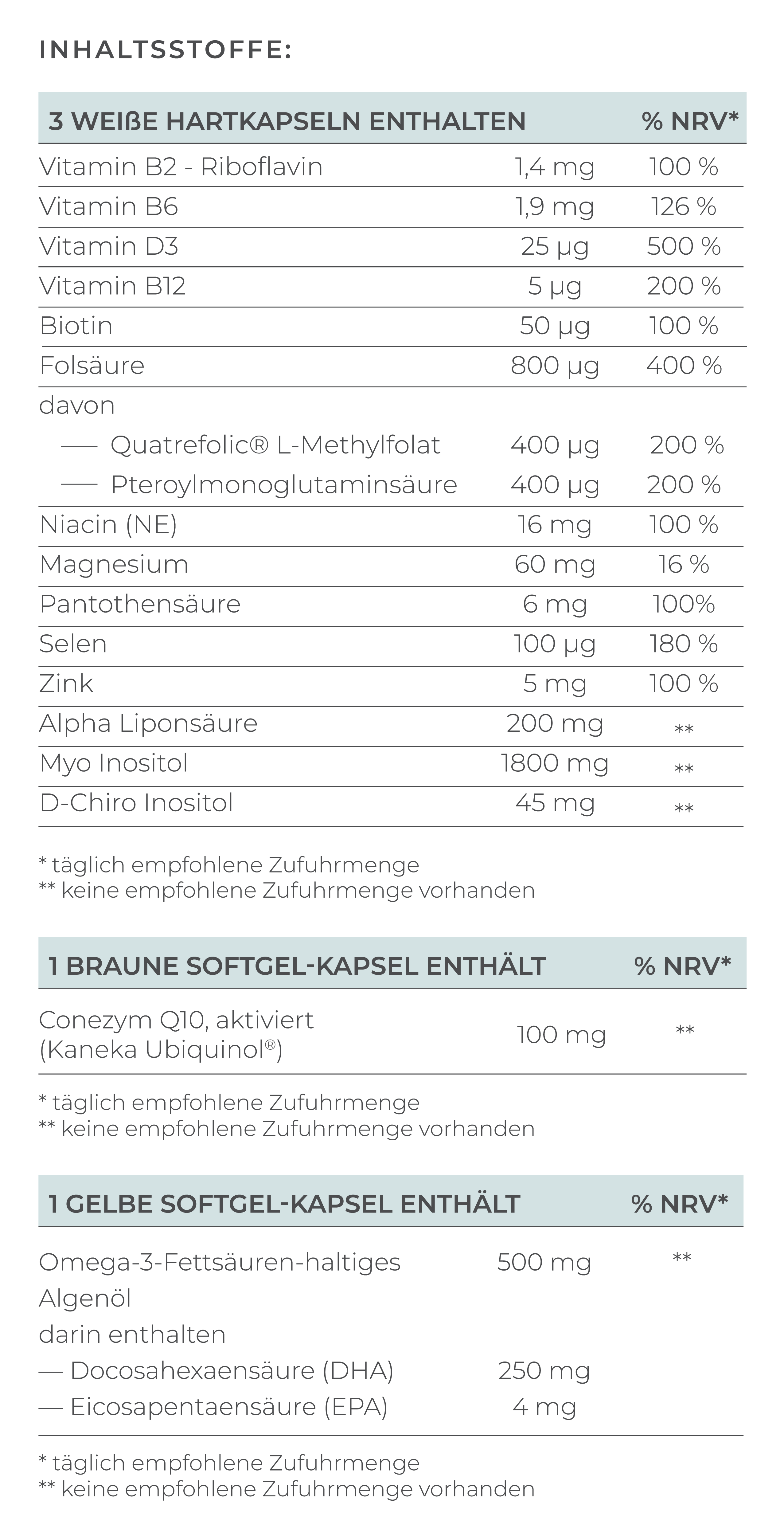
- Coenzyme Q10 in the form of ubiquinol for follicle maturation
- Omega-3 fatty acids with at least 250mg DHA for anti-inflammatory effects
- Antioxidants such as alpha-lipoic acid and selenium to protect the eggs from oxidative stress
- Myo-inositol to support ovarian function and a regular menstrual cycle
- Folate, the bioavailable form of folic acid, for cell division
Important nutrients for men are:
- Omega-3 fatty acids for anti-inflammatory effects and increased testosterone levels
- Antioxidants such as trans-resveratrol, myo-inositol to protect sperm cells
- Folate, the bioavailable form of folic acid, for cell division
Which Treatments Help with Unwanted Childlessness?
If you haven’t become pregnant after a year of regular intercourse or have had two or more miscarriages, you and your partner should seek help at a fertility clinic.
Medication Treatment
- Hormone treatments: Hormonal stimulation of the ovaries can help improve follicle maturation and trigger ovulation. For thyroid disorders, treatment with thyroid hormones should be done to optimize the TSH level.
- Treatment of underlying conditions: If a condition like endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the cause of infertility, treating it can increase the chances of pregnancy.
Artificial Insemination
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI is often the first fertility treatment recommended for mild fertility issues. Fertile sperm is directly inserted into the uterus to increase the chances of pregnancy.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is typically used for female fertility issues, such as endometriosis or blocked fallopian tubes. After hormonal stimulation, as many eggs as possible are retrieved, fertilized in the lab with prepared sperm, and the embryos are transferred into the uterus after 2-5 days.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): During ICSI, a single sperm cell is injected directly into an egg. This method is often used for male infertility.
Further Diagnostics
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions such as endometriosis or blocked fallopian tubes.
- Hysteroscopy: A procedure where a thin, illuminated instrument is inserted into the uterus to diagnose and treat abnormalities.
- Genetic counseling: If you've experienced infertility for a while, are undergoing assisted reproduction, or have had multiple miscarriages, genetic counseling involving chromosome analysis and genetic testing may be helpful.
Emotional Support When Facing Infertility
The waiting period can be an exceptional and stressful time for most couples, both physically and emotionally—it can affect health, relationships, and overall well-being. Therefore, psychological support or counseling in fertility clinics, counseling centers, support groups, or even online forums is recommended to provide comfort during these tough times.
While psychological issues are not usually the cause of infertility, they can become a result of it. The field of gynecological psychology was founded to explore the connection between mental health, stress, and infertility, helping couples with their desire for children or supporting them in starting a new chapter of life. In support groups, sensitive topics can be openly discussed without fear of stigmatization, allowing shared experiences and new perspectives to provide hope.
The Best Moms Are Not Moms Yet
A missed pregnancy can be one of the greatest challenges in a couple's life. Despite the difficulties, there are ways to cope with infertility and possibly still fulfill the dream of having a child. Couples trying to conceive can openly discuss their feelings, seek professional support, adjust their lifestyles, and practice self-care to increase their chances of becoming parents. Parenthood can be defined in many ways. The best moms are not moms yet.
FAQ
What are my chances of pregnancy per cycle?
A study examined the change in fertility based on reproductive age and found that the likelihood of pregnancy per cycle for women aged 19-26 is about 25% (Dunson, 2002). For women aged 30-34, the likelihood is about 20%, and it decreases to about 15% for women aged 35-39.
What is the best age to get pregnant?
There is no "best" age to get pregnant, as it depends on individual circumstances. However, a woman’s fertility is highest in her 20s and decreases with age, especially after her mid-30s.
How long does it take to get pregnant?
There is no universal answer to how long it takes to get pregnant. It depends on many factors, such as the age and health of both partners, their lifestyle, and chance. A German study (Gnoth, 2003) examined how long it takes couples to conceive:
- 80-90% of couples conceive within 12 months: This means that most couples will become pregnant within a year if they have regular unprotected intercourse.
- 60% conceive within 6 months: Half of the couples will even conceive within six months.
The study also showed that a woman’s age influences the time to pregnancy, with younger women tending to conceive faster than older women.
Does health insurance cover fertility treatments?
The coverage of fertility treatments varies in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.
- In Germany, statutory health insurance is required to cover 50% of the costs for IVF or ICSI under certain conditions. Importantly, coverage is only available to married couples.
- In Austria, fertility treatment costs are not covered by health insurance. However, through the IVF fund, couples can receive reimbursement for 70% of the treatment costs.
- In Switzerland, basic insurance covers the cost of three IUI cycles per pregnancy attempt for insured couples. IVF or ICSI costs must be covered by the couple unless they have supplementary insurance.
References
Bongaarts et al. Fertility Transition in the Developing World. Springer, 2022.