Key points at a glance
- For successful implantation, the endometrium must be receptive. This occurs during a period of 2-6 days, known as the "implantation window."
- If pregnancy does not occur despite good embryo quality after several IVF/ICSI cycles, it is referred to as repeated implantation failure (RIF).
- About 10% of couples undergoing IVF/ICSI treatment are affected by implantation disorders.
- The causes can be related to the woman (e.g., blood clotting disorders, anatomical changes in the uterus), the man (e.g., sperm quality), or the embryo itself (e.g., genetic abnormalities).
- In about 30% of couples with unexplained infertility, no cause can be found despite extensive investigation.
Embryo Implantation
Implantation is the attachment of the embryo to the uterine wall during the implantation window, approximately 6 to 7 days after fertilization.
During the implantation window, a period of around 2 to 6 days, the endometrium (uterine lining) typically provides optimal conditions for implantation. It is important that the embryo reaches the blastocyst stage and hatches from its shell exactly at this moment of receptivity.
Repeated implantation failure is both a medical and emotional challenge for couples trying to conceive. It can lead to infertility and the associated suffering, as well as increase the risk of repeated miscarriages.
When is it considered recurrent implantation failure (RIF)?
Recurrent implantation failure (RIF) occurs when, despite multiple attempts with high-quality embryos in artificial fertilization, no pregnancy occurs.
How common are implantation disorders?
About 10% of couples undergoing IVF treatment or ICSI are affected by repeated implantation failure. (Ma et al., 2023)
Causes of implantation failure
The causes can be diverse, and the issue of implantation failure is not yet fully understood.
The following factors can influence implantation.
Maternal factors
- Coagulation disorders (Thrombophilia, e.g., caused by antiphospholipid syndrome)
- Immunological disorders, such as elevated killer cells in the blood or uterus
- Anatomical changes of the uterus, such as polyps or fibroids
- Endometrial infections, i.e., infections of the uterus (Endometritis)
- Poor egg quality, for example, due to endometriosis or maternal age
- Genetic predisposition
- Anomalies in the implantation window
Paternal factors
- Sperm quality
- DNA fragmentation of sperm
- Genetic predisposition
Embryo factors
- Reduced embryo quality
- Delayed development
- Genetic changes in the embryo
Recommended tests
To identify the causes of repeated implantation failure, various tests can be conducted.
Please note that not every fertility center offers the full range of tests. Some centers specialize in specific areas of reproductive medicine and may not have the necessary equipment or expertise for all tests, such as polar body diagnostics or the ERA test.
- Genetic testing of the couple: A blood test is used to examine the genetic material of both partners for chromosomal abnormalities that may affect embryo development and lead to implantation failure.
- Sperm DNA fragmentation analysis: A sperm analysis can be used to assess DNA damage in sperm that may negatively impact fertilization and embryo development.
- Immunological assessment: A blood test examines various parameters of the immune system to rule out autoimmune diseases or immune reactions that could prevent embryo implantation.
- Coagulation disorder assessment (Thrombophilia): Coagulation disorders can impair blood supply to the endometrium, affecting implantation. A blood test can detect these disorders and allow treatment before embryo transfer.
- Infection screening: Certain infections, such as sexually transmitted diseases or cytomegalovirus, can prevent embryo implantation or lead to early miscarriage.
- Hysteroscopy and endometrial assessment (surgical procedure): The uterine cavity is examined with an endoscope to rule out anatomical anomalies like fibroids, polyps, or adhesions that may hinder implantation. The endometrium is also assessed for its structure and suitability for implantation.
- Endometrial Receptivity Test (ERA, Endometrial Receptivity Array): This test analyzes gene expression in the endometrium to determine the optimal time for embryo transfer and increase the likelihood of implantation.
- Polar body diagnostics of the embryo: This genetic test examines the polar bodies of the egg to detect chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo before transfer.
Unfortunately, in some couples, no cause can be identified despite a complete investigation (idiopathic infertility). About 30% of couples with unexplained infertility are affected by this (Sadeghi, 2025).
Treatment options
Extended cultivation to the blastocyst stage
In the context of fertility treatment, embryos can be cultured up to the blastocyst stage (Day 5 after egg retrieval), allowing for close observation of their development. This enables the selection of the best embryo to increase the chances of implantation.
Heparin treatment
In women with coagulation disorders, treatment with heparin is recommended. This is usually administered through injections until the 12th week of pregnancy or throughout the entire pregnancy.Antioxidants for egg quality
A healthy egg forms the foundation for a high-quality embryo. Optimal conditions during the maturation of the follicle and the egg it contains are crucial for egg quality.
In the natural metabolism, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced, which can damage cells and genetic material. Cells have mechanisms to neutralize these molecules, but when ROS levels are elevated, the cell may become overwhelmed—this is oxidative stress. Life stress, in particular, increases this ROS level.
A high concentration of ROS can reduce egg quality, affect the aging process, and lower fertilization and implantation chances.
Antioxidants can neutralize ROS and positively influence egg quality (Tamura et al., 2008). Therefore, taking antioxidants in high-quality fertility supplements before egg retrieval is recommended.
Assisted Hatching
For embryos with a thickened zona pellucida, a hole is punctured to facilitate the hatching of the embryo.
Infusion Therapy
In certain cases, infusion therapy with the active ingredients DHA and EPA from omega-3 fatty acids can show anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. One study found that women with repeated implantation failure and an elevated TH1 cytokine response had a pregnancy rate of 50% and a clinical pregnancy rate of 46% after intralipid infusions (Fatemi et al.).
Conclusion
Repeated implantation failure is a significant medical and emotional challenge. Despite high embryo quality after several IVF/ICSI cycles, pregnancy does not occur in about 10% of couples. The causes can be diverse and may be attributed to maternal, paternal, or embryonic factors. Despite comprehensive investigations, the cause remains unknown in about 30% of couples.
For successful implantation, the receptivity of the endometrium is crucial, which occurs during the so-called "implantation window." Repeated implantation failure can also increase the risk of repeated miscarriages.
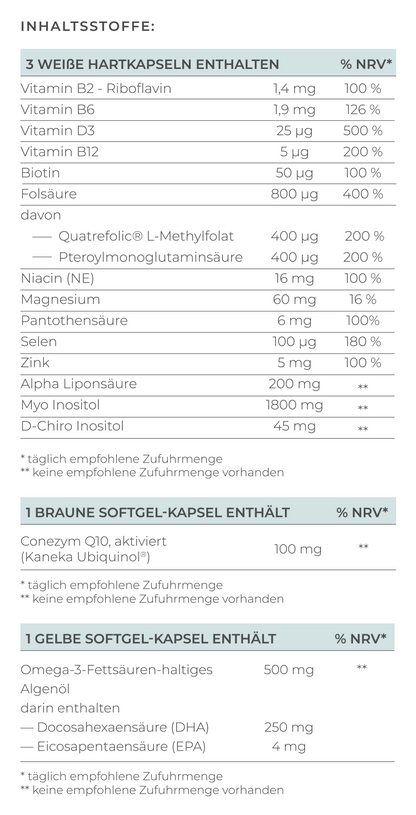
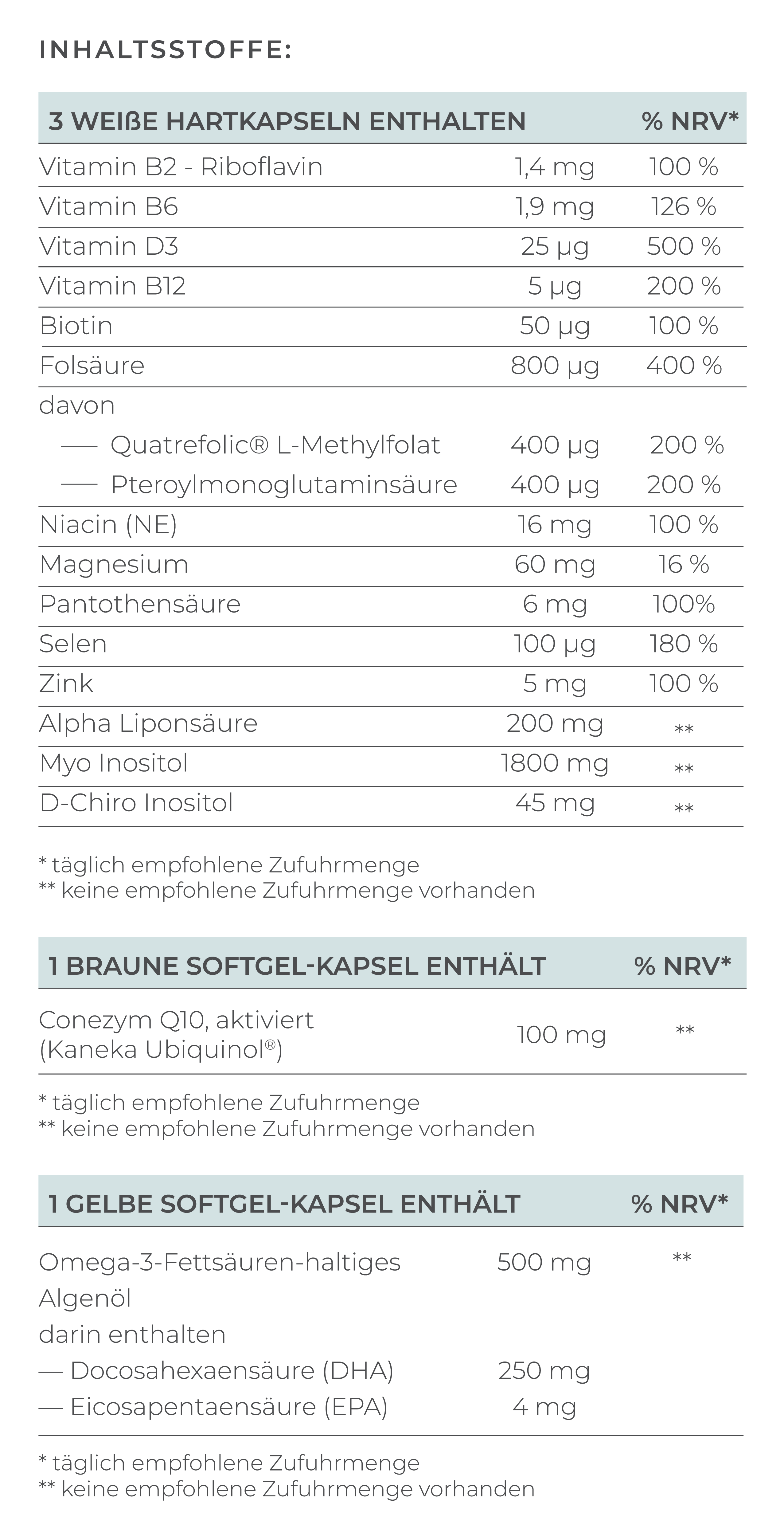
Although the reasons for implantation disorders can be varied, VILAVIT Female can help improve egg quality and thus increase the chances of successful implantation.