Key Points at a Glance
- Micronutrients like Ubiquinol, Myo-Inositol, and Vitamin D support fertility.
- Stress reduces fertility, so practicing relaxation is important.
- Try tracking your fertile days.
- A healthy diet and exercise improve fertility.
- Avoid alcohol and nicotine for better chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Getting Pregnant: Everything You Need to Know
A shot and a hit – unfortunately, getting pregnant is not always that fast. While romantic comedies might suggest that even a one-night stand guarantees a baby, reality is different: A large European study found that the average time to conceive is about 4 to 6 months (Slama et al., 2002). Even after this time, there’s no need for concern. About 15% of couples take more than a year to conceive – even under optimal conditions, with fertile partners and an age under 38. However, we don’t want to wait that long.
Here are five tips to help speed up the process, increase your chances of conception, and hopefully have you celebrating a positive pregnancy test soon!
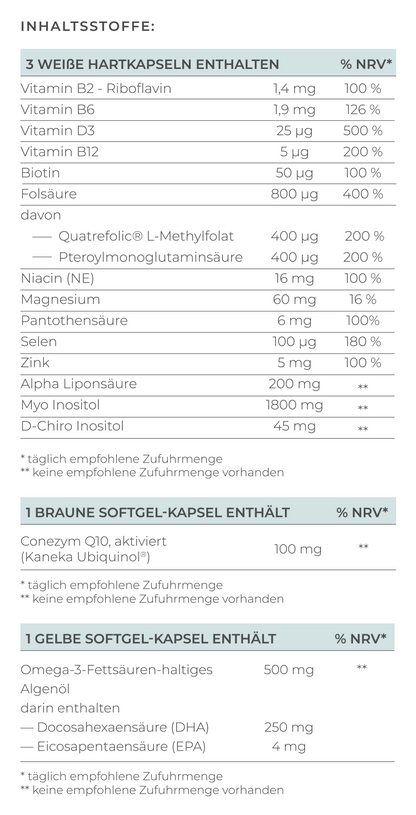
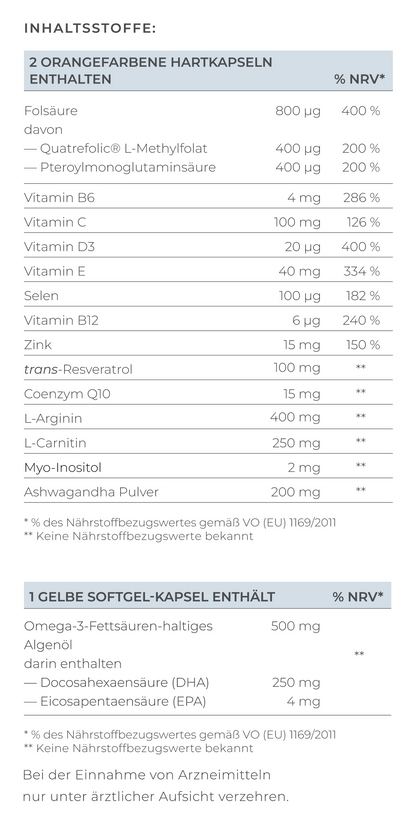
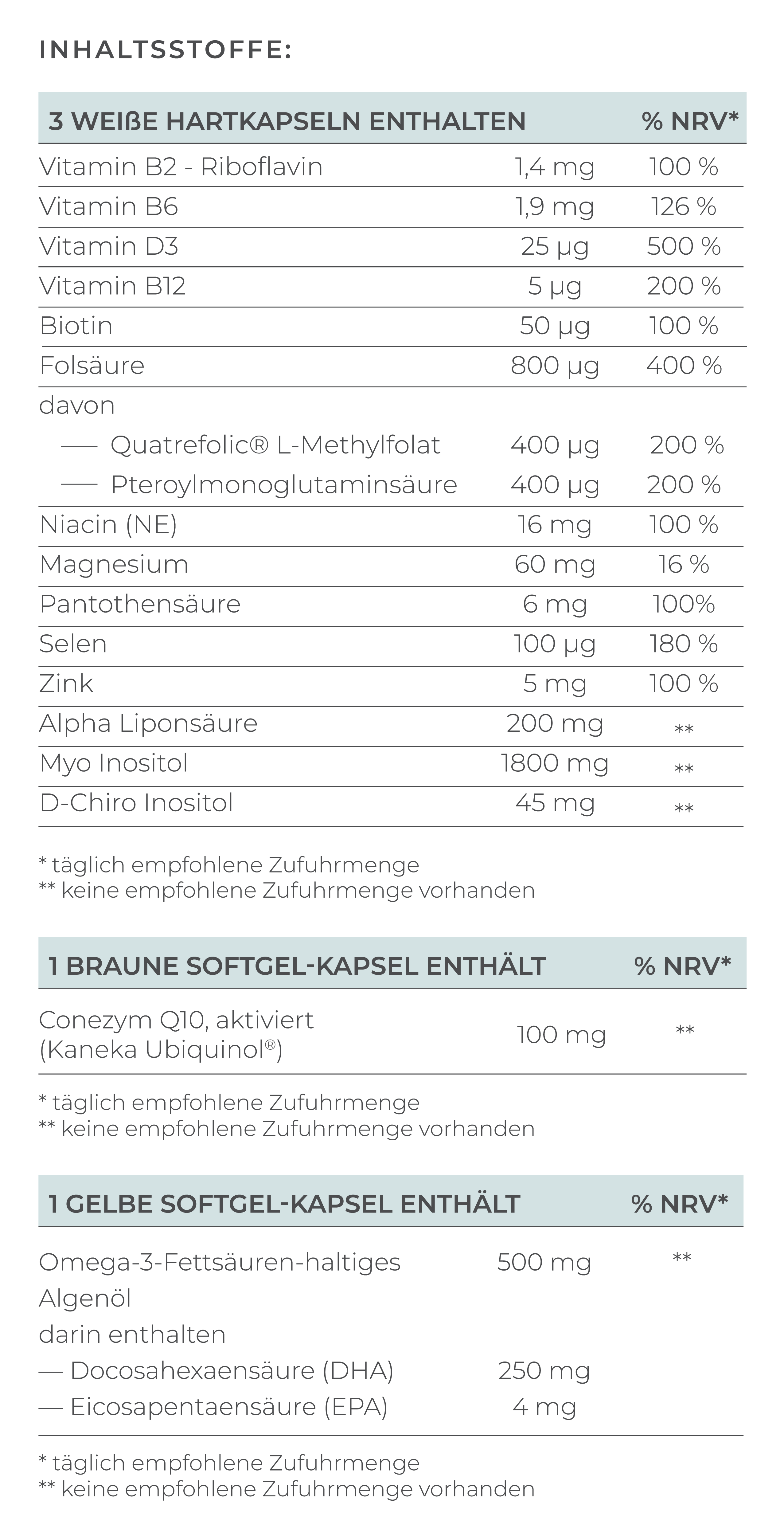
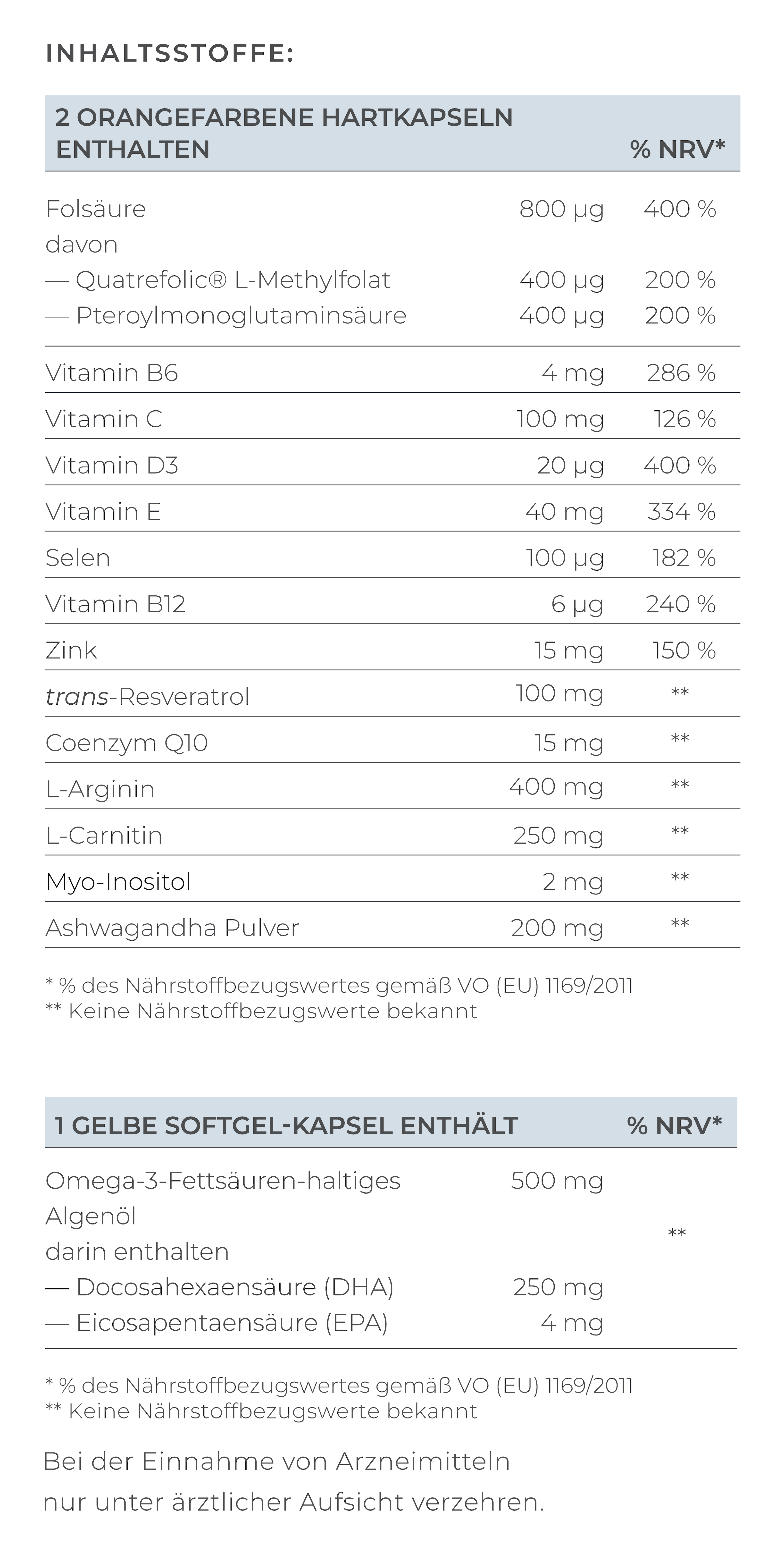
1. Support Your Body with Micronutrients
Micronutrients improve egg quality, reduce the risk of miscarriage, and support cell division – and these are specific micronutrients.
However, due to changing dietary habits and decreased nutrient density in foods, some nutrients can no longer be obtained solely through food.
In this case, it's wise to take the following supplements:
- Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinol): This important antioxidant protects cells from harmful free radicals and supports the mitochondria, the "powerhouses" of cells. It also helps with egg maturation, which is crucial for successful fertilization and a healthy pregnancy. Studies have shown that women who took 30 mg of Ubiquinol daily for eight weeks before IVF treatment had more fertilizable eggs, more fertilized eggs, and higher-quality embryos compared to those who didn’t take Ubiquinol (Lin et al., 2023).
- Myo-Inositol: Myo-Inositol is an isomer of glucose, particularly important for regulating hormones that control the menstrual cycle. Women with hormonal imbalances, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), can benefit from Myo-Inositol as it helps stabilize the cycle by normalizing hormone production and release. Studies show Myo-Inositol can improve fertility and promote a regular cycle. One study found that Myo-Inositol positively influenced the LH and FSH hormone ratio, leading to a more stable cycle (Gerli et al., 2007).
- Vitamin D: This vitamin is essential for brain, immune system, organ, skeletal development, and metabolism in the fetus. Even before pregnancy, it can help increase fertility, as evidence suggests Vitamin D impacts egg quality. A study found that women with higher Vitamin D levels had better fertilization rates, higher top embryo rates, and higher pregnancy rates (Ciepiela et al., 2018).
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): A powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage by free radicals. It helps reduce the aging-related strain on eggs and can improve egg quality. ALA also has positive effects on insulin sensitivity, which can be particularly beneficial for women with PCOS (Abu-Zaid et al., 2024).
2. Avoid Stress
Stress, both short-term and long-term, can significantly affect fertility. Acute stress can lead to increased production of stress markers like cortisol and alpha-amylase. High stress levels, measured by alpha-amylase in saliva, have been linked to longer wait times for pregnancy and an increased risk of infertility (Lynch et al., 2014).
Chronic stress, lasting over a longer period, can lead to hormonal changes that disrupt the menstrual cycle and hinder ovulation (Lewinski et al., 2023).
While we often hear "the fertility journey is stressful," the emotional burdens of infertility can cause significant stress. To escape this cycle, it's essential for couples to seek emotional support from support groups or fertility coaches, and integrate stress-reduction strategies like meditation, yoga, or exercise into their daily routine.
3. Track Your Fertile Days
Even for fertile couples, the chance of getting pregnant naturally per cycle is only about 20-30% (Gnoth et al., 2005). This figure comes from extensive studies on natural fertility, showing that even under optimal conditions, the chances per cycle are limited. To maximize your chances, it's crucial to target your fertile days, which are the days before and during ovulation. A study by Wilcox et al. (1995) found that the most fertile days in a cycle are the five days leading up to and the day of ovulation. Using a cycle tracker or ovulation calculator can help you better understand your cycle and pinpoint your most fertile days.
4. Pay Attention to Proper Nutrition & Exercise Regularly
A healthy lifestyle provides your body with essential micronutrients, reduces stress, and gives you the energy to successfully handle both daily life and family planning. Studies show that a balanced, vitamin-rich diet can positively impact fertility. For example, one study showed that a "fertility diet" rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can reduce cycle-related infertility (Chavarro et al., 2007). Regular exercise, especially moderate endurance training, has been shown to be beneficial for fertility. One study found that women who stay physically fit have a higher likelihood of getting pregnant (Rich-Edwards et al., 2002).
5. Avoid Alcohol & Nicotine
Alcohol and nicotine have significant negative effects on female fertility. Regular alcohol consumption can disrupt hormone balance and affect the menstrual cycle, thereby reducing the chances of successful conception. One study showed that women who consumed more than seven alcoholic drinks per week had an increased risk of infertility (Tolstrup et al., 2003).
Nicotine is particularly harmful to female fertility. Smoking can reduce the quality and quantity of eggs and accelerate the loss of ovarian reserve, which increases the risk of early menopause (Augood et al., 1998). Additionally, nicotine consumption can significantly lower the success rates of fertility treatments like IVF.
These two toxins are dangerous not only during pregnancy but also beforehand. Therefore, it’s recommended to avoid alcohol and nicotine for at least three months before planning pregnancy.
Conclusion
To increase your chances of conception, it’s essential to support your body optimally – whether through micronutrients, a healthy diet, or stress-reducing measures. Targeting fertile days and avoiding alcohol and nicotine can also make a significant difference. Every woman and couple is unique, but with these tips, you can enhance natural processes and boost your chances of pregnancy. Patience and mindfulness with your body are key on your journey to conception.
FAQ
How can I get pregnant despite having an irregular cycle?
An irregular cycle can make conception more challenging. First, it's important to determine the cause of your irregular period through a medical examination. Hormonal imbalances, such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), are common culprits affecting cycle regularity. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction can also help stabilize the cycle. If needed, medications or supplements like Myo-Inositol can regulate the cycle and boost fertility. Ovulation tests, cycle trackers, or basal temperature measurements can help identify fertile days.
Are there tips for men who want to get pregnant quickly?
To improve the chances of a quick pregnancy, it’s advisable for men to have their fertility checked by a doctor. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are crucial. Alcohol, nicotine, and drug use should be avoided, as well as heat exposure from hot baths or tight clothing, as they can negatively affect sperm production. Stress reduction techniques like meditation or yoga can also be beneficial. Additionally, micronutrients like those found in VILAVIT Male can improve sperm quality and support fertility.
How long does it take to get pregnant at 40?
At 40, the likelihood of conceiving in any given cycle is about 5-10%, as egg quality decreases with age. It’s advisable to consult a doctor early to assess your individual situation and possibly consider options like assisted reproduction.
References
Lin, Y., et al. (2023). "Effect of Ubiquinol supplementation on oocyte and embryo quality in women undergoing IVF: A randomized controlled trial." Journal of Reproductive Medicine