-
The sperm count has fallen by over 50% since the 1970s.
-
Male fertility issues account for approximately 40% of all infertility cases.
-
Sperm cell disorders are a central cause of male fertility problems.
-
The diagnosis ranges from a hormone status to a spermiogram and DNA questionnaire test.
-
Treatment options include fertility supplements, lifestyle changes and fertility treatments.
Male Infertility: The Taboo
-
The average sperm count has fallen by over 50% since the 1970s and continues to fall by around 1% each year, a decline that is observed regardless of the man's age. Male fertility is the cause of around 40% of unfulfilled childlessness. Despite these figures, the topic of male infertility is often still taboo and receives too little attention.
-
According to the World Health Organization, infertility occurs when a man is unable to conceive a child within a year despite regular, unprotected sexual intercourse (on the woman's fertile days).

You are not alone!
You are not alone! This is an important message. Fertility challenges affect many men around the world, even though they are often little talked about. Numerous factors can contribute to this, and it's completely understandable if these challenges are weighing you down. In addition to medical care and emotional support, a targeted supply of micronutrients also plays a crucial role in sustainably strengthening male fertility.
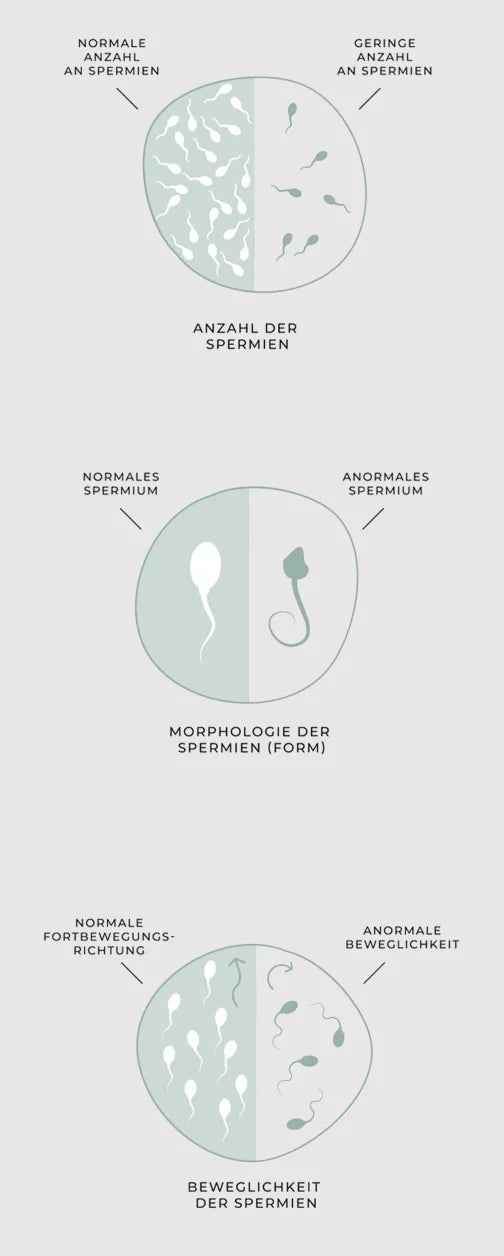
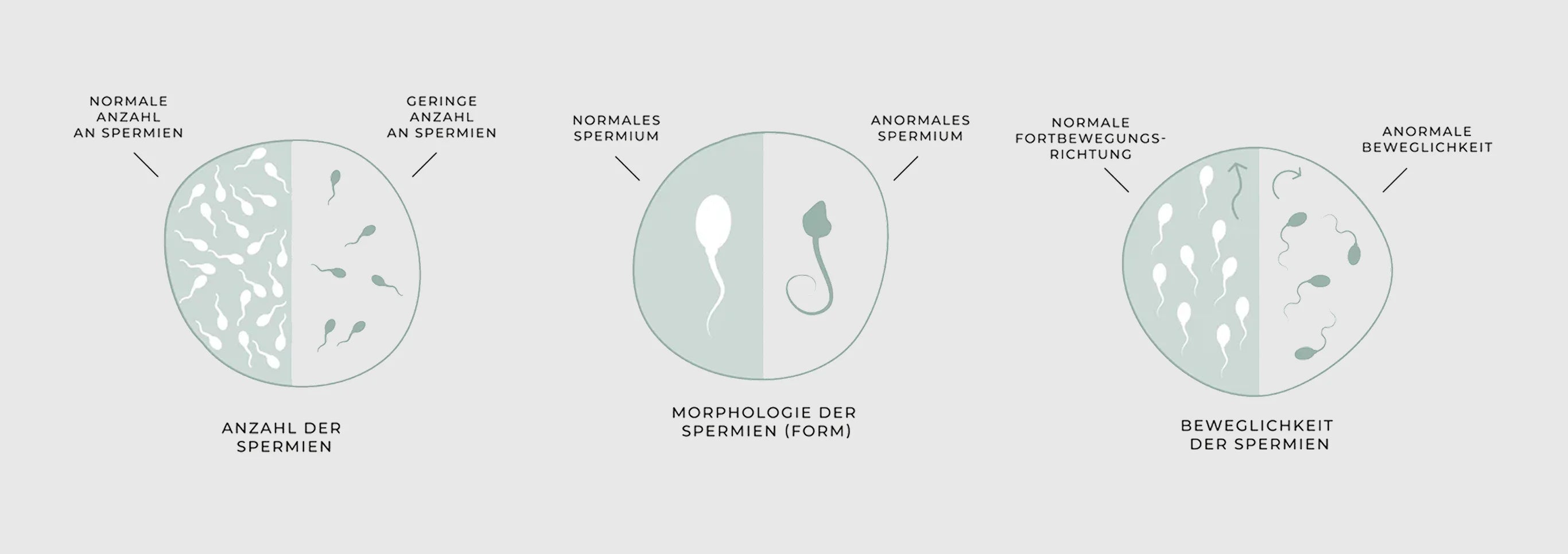
Sperm production disorder
Sperm disorders are a major cause of male fertility problems and contribute significantly to the unfulfilled desire to have children. For successful fertilization, the sperm must be able to reach the egg. Various abnormalities can significantly impair the functionality and quality of the sperm.
-
Reduced sperm count
OLIGOZOOSPERMIA
Oligozoospermia, i.e. a reduced number of sperm in the ejaculate, reduces the likelihood of enough healthy sperm reaching the egg. This significantly limits male fertility.
-
Reduced number of motile sperm
ASTHENOZOOSPERMIA
Asthenozoospermia, a reduced motility of the sperm, makes it difficult for the sperm cells to advance in the female genital tract and reach the egg cell. Targeted forward movement is crucial for the path to the egg cell.
-
Reduced number of normally formed sperm cells
TERATOZOOSPERMIE
The shape of the sperm determines its ability to fertilize an egg. A normally shaped sperm has an oval head, an energy-producing middle section and a long, slender tail for targeted movement. Only such sperm can swim efficiently through the female genital tract, penetrate the egg membrane and trigger fertilization.
-
Disruption of transport routes
AZOOSPERMIAA
Disorder of the transport pathways occurs when the sperm ducts are blocked or narrowed, for example due to adhesions, scarring or obstructions. As a result, the sperm produced in the testicles cannot reach the ejaculate. This blockage leads to a complete absence of sperm in the ejaculate.
Hormone diagnostics also play an important role in the clarification of an unfulfilled desire to have children in men. Hormonal imbalances can significantly impair sperm production and quality and thus limit fertility. A comprehensive hormone examination is therefore recommended, particularly in the case of reduced sperm quality. Typical signs of a possible hormonal imbalance are persistent tiredness, fatigue, a noticeable loss of vitality, unexplained weight gain and a general reduction in performance. These symptoms indicate that important hormones such as testosterone, FSH or LH are not in the optimum range. A blood sample is taken for clarification.
The most important examination method for assessing male fertility is the spermiogram. This is the microscopic analysis of the ejaculate. It provides information on sperm quality, sperm count and sperm density. The amount of fluid (volume) and the pH value of the ejaculate are also determined. The ejaculate should be obtained by masturbation after a waiting period (time without ejaculation) of two to seven days. It must be collected under sterile conditions and ideally in the laboratory on site, or no more than 30-60 minutes away. At least two spermiograms over a period of four to twelve weeks are recommended, as the number and quality of sperm cells can vary greatly.
The task of the sperm is to safely transfer the father's genetic information to the egg. As a result, a healthy embryo can develop. However, a DNA break, i.e. damaged genetic information in the sperm, can mean that new cells and therefore also an embryo cannot develop. Although a spermiogram does not show any abnormalities, fertility can still be limited as it does not show any conclusions about possible breaks in the sperm's DNA strand. Various test options (TUNEL or SCD test) allow the genetic material of the sperm to be analyzed using a semen sample. There are currently no standardized guideline values, but 15-20% slightly to moderately fragmented sperm lead to reduced fertility.
Causes of Male Infertility
Undescended testicles
During childhood, the testicles do not migrate correctly into the scrotum, but remain in the abdomen or groin area. Later sperm production is permanently damaged if undescended testicles are not corrected in time.
Infections
A mumps infection (mumps orchitis) in a child can result in testicular inflammation and hardening. This is accompanied by severely restricted sperm production later on.
Testicular varicose vein
The spermatic cords in the testicles are surrounded by a network of veins. If this becomes enlarged, this is referred to as a varicose vein in the testicles, also known medically as a varicocele. The left side of the testicle is usually affected, as this is where the blood drains less easily. The strong build-up of heat due to the backed-up blood in the testicle area affects fertility.
Nutrient deficiency
An optimal supply of nutrients is of central importance for male fertility, as a lack of important nutrients can significantly impair the quality and quantity of sperm. Coenzyme Q10, trans-resveratrol, L-arginine, L-carnitine and omega-3 fatty acids are essential for healthy sperm production and function.
VILAVIT Male is a specially developed fertility supplement that contains all the important active ingredients in a high-quality form and optimal dosage. That's how we support men in improving their fertility.
Hormonal disorders
Hormonal disorders can also lead to infertility in men. The following hormones are particularly important for the formation of new sperm: testosterone, FSH and LH. A deficiency can limit male fertility.
Genetic defects
These include Klinefelter syndrome with reduced secretion of male hormones and reduced sperm quality. There is also deletion, the loss of information on the Y chromosome, which is responsible for male sexual expression. Genetic defects can be identified by means of a blood test.
Age
Age also plays an important role in fertility in men. From the age of 35, sperm quality declines. There is an age-related reduction in motility and sperm count. In addition, more chromosomal changes (DNA fragmentation) occur in the individual sperm cells.
Other risks
There are many causes of reduced fertility in men. Pre-existing conditions, often in childhood, such as infections, inflammation of the (epididymis) testicles, urinary bladder or prostate can affect male fertility, but additional risk factors include stress, eating habits, obesity, taking certain medications, alcohol and nicotine consumption and other environmental factors. Increased temperature in the testicle area can also have a negative effect on fertility (e.g. due to prolonged sitting, heated seats, saunas, etc.).
Diagnosis
In the case of infertility, the initial focus is often on examining the woman, while the man is often only examined after a delay. An early examination of the man is just as important and can save valuable time. The diagnosis of fertility disorders in men is carried out by a specialist in reproductive health, the andrologist, an expert in the field of urology. The following examinations and analyses provide important information on male fertility:
Therapy for Male Infertility
Medical Treatment
Lifestyle Changes

Improve your Sperm Quality
Numerous medical studies have shown that the targeted intake of specific micronutrients can sustainably improve male fertility. Coenzyme Q10, trans-resveratrol, L-arginine, L-carnitine and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly important for increasing sperm production and quality. The targeted supplementation of these active ingredients improves both sperm quality and sperm count. This significantly increases the chances of successful conception.














VILAVIT Male
- Regular price
-
€69,00 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
€69,00
Usage
It is recommended to start taking VILAVIT Male at least three months before the planned conception. This corresponds to the period of spermatogenesis, the process of formation and maturation of sperm cells, which takes around 70 to 90 days. During this time, new sperm cells develop, which can be supported in the best possible way by a targeted supply of micronutrients. Early supplementation helps to promote the quality of sperm cells in the long term.
Recommended intake
- Recommended intake: 1 sachet (contains 3 capsules) daily.
- Open the sachet and swallow each capsule individually with plenty of water.
- Not suitable for children and adolescents.
Our quality promise
Manufactured to the highest quality and production standards
Tested by external experts
Made in Austria